 |
| Integrated generic resource: Visual presentation | ISO 10303-46:2021(E) © ISO |
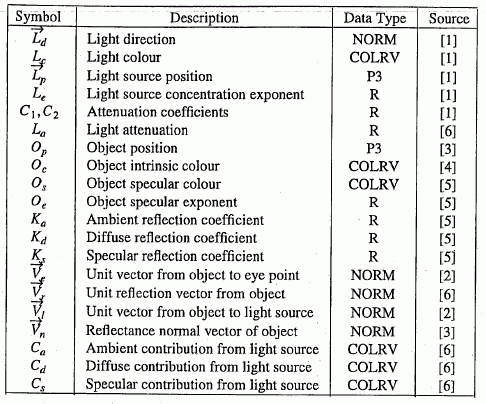
Table E.1 is taken from ISO/IEC 9592-1:1997, Annex H.
Table E.1 — Variable definition and their sources
 |
Source Legend:
[1] Light source representation
[2] Calculated
[3] Explicit or derived from object geometry
[4] Source of intrinsic colour (ISO/IEC 9592-1:1997 table 18, 4.5.8.5)
[5] Reflectance properties
[6] Calculated per formulae given in E.2.
E.2 Reflection formulaeThe following equations are taken from ISO/IEC 9592-1:1997, Annex H.
The result of the reflectance formulae evaluated at the point on a primitive is a single colour that is the sum of the individual components C a +C d +C s of all the currently active light sources, as follows.
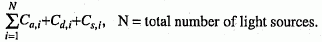
For ambient light sources
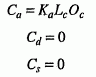
For directional light sources
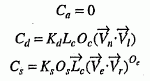
For positional light sources
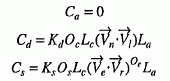
For spot light sources: (Contributions from one spot light sources will be zero if O p is outside the cone of influence of the light source.)
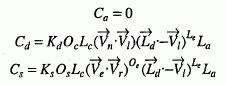
Light attenuation may be calculated as follows:
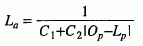
where |O p -L p | is the distance between the object and the light source. The reflection vector may be calculated as follows:
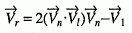
In the calculation of C d and C s , a dot product resulting in a negative number is replaced by 0. In the calculation of
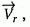
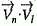
For interior shading method 3 (DATA) the quantities
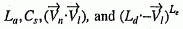
For interior shading method 4 (DATA and DOT) the quantities
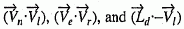
© ISO 2021 — All rights reserved